Cloud computing offers businesses incredible scalability, flexibility, and agility. However, as more organizations migrate to the cloud, many are experiencing “cloud sticker shock” — unexpected costs that spiral out of control as cloud usage grows. The reality is that managing cloud costs can be just as complex as managing traditional infrastructure. But don’t worry — with the right strategies and tools, you can optimize your cloud spending and maximize the value of your cloud investment.
In this blog post, we’ll explore effective cloud cost optimization strategies that help organizations avoid waste, optimize resources, and take full advantage of cloud scalability without breaking the bank.
Why Cloud Cost Optimization Matters
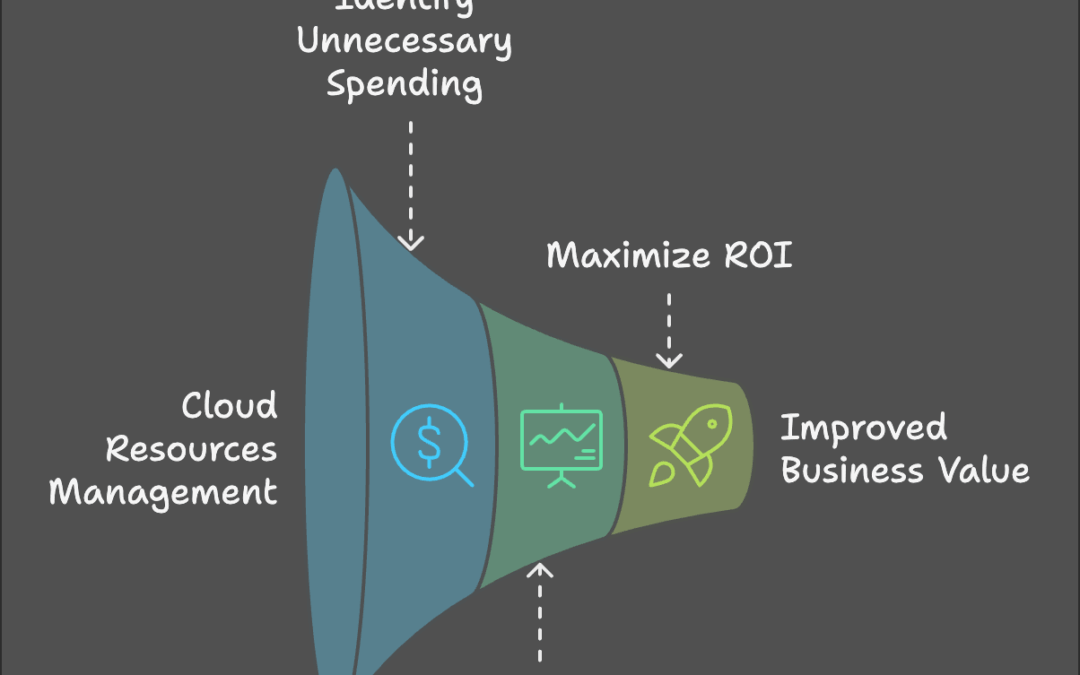
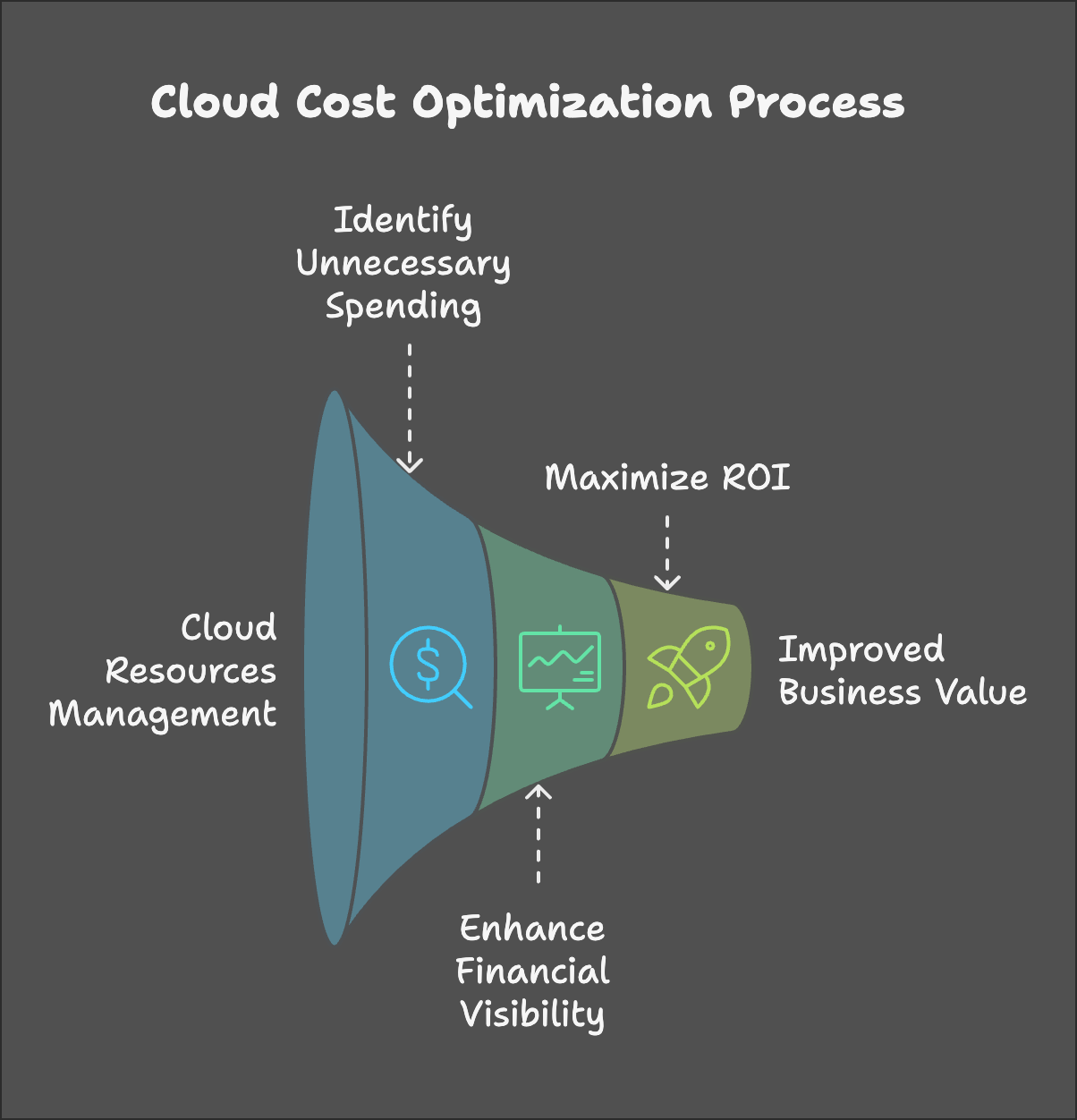
Cloud cost optimization is not just about slashing budgets — it’s about getting more value from every dollar spent. When implemented correctly, cloud cost optimization ensures that resources are being used efficiently, allowing businesses to scale without overspending. It also helps organizations avoid the risk of “cloud sprawl,” where unused or underutilized resources accumulate over time and increase costs unnecessarily.
Here are some key reasons why cloud cost optimization should be a priority:
- Avoiding Unnecessary Spend: It’s easy to over-provision resources or leave services running that aren’t actively being used. Cloud cost optimization helps identify and eliminate this waste.
- Improving Financial Visibility: Properly tracking and analyzing cloud expenses helps businesses understand where money is being spent and why.
- Maximizing ROI: By improving efficiency, businesses can derive more value from their cloud investments and use those savings to fund innovation and growth.

Top Strategies for Optimizing Cloud Costs
- Right-Sizing Your Resources
- What It Is: Right-sizing refers to matching the allocated resources (e.g., CPU, memory, storage) to the actual needs of your applications or workloads.
- How It Helps: Underutilized resources are a major source of waste. By adjusting your resource allocation to the right size — based on actual usage patterns — you ensure you’re not overpaying for capacity you don’t need.
- Tools: AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, Google Cloud’s Recommender tool.
- Leverage Auto-Scaling
- What It Is: Auto-scaling automatically adjusts the number of active resources based on current demand. It’s a fundamental feature in cloud environments that ensures you’re only using and paying for what you need at any given time.
- How It Helps: This strategy prevents over-provisioning and ensures that resources scale up or down dynamically, depending on the workload, without manual intervention.
- Example: If your web application experiences spikes in traffic during certain times, auto-scaling ensures additional resources are allocated during peak periods and deallocated when the load decreases.
- Take Advantage of Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
- What It Is: Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer discounted pricing models for long-term usage. These pricing plans require you to commit to a specific level of usage over a period (1 year, 3 years, etc.).
- How It Helps: Reserved instances and savings plans can provide significant discounts — sometimes up to 75% off pay-as-you-go prices — if your workloads have predictable usage patterns.
- Example: If your company consistently runs a certain instance type 24/7, you can lock in a lower price by committing to a reserved instance, significantly reducing costs over time.
- Use Spot Instances for Non-Critical Workloads
- What It Is: Spot instances (or Preemptible VMs in Google Cloud) are unused compute capacity that is available at a fraction of the cost of on-demand instances.
- How It Helps: Spot instances can be a great option for workloads that are fault-tolerant, such as batch processing, data analysis, or other non-critical tasks.
- Example: AWS EC2 Spot Instances and Azure Spot Virtual Machines allow you to bid for unused capacity, often reducing costs by 90% compared to standard on-demand pricing.
- Implement Cloud Cost Monitoring and Alerts
- What It Is: Setting up cloud cost monitoring allows you to track and manage expenses in real-time. Most cloud providers offer dashboards and alerting mechanisms that can notify you when your spending is exceeding predefined thresholds.
- How It Helps: Continuous monitoring ensures you stay within your budget, and real-time alerts can help identify anomalies or spikes in usage before they turn into major cost overruns.
- Tools: AWS Budgets, Azure Cost Alerts, Google Cloud’s Budget and Alerts.
- Consolidate Accounts and Use Organizational Discounts
- What It Is: Many cloud providers offer discounts when multiple accounts are consolidated into a single organization. This could include volume discounts or shared usage across teams.
- How It Helps: By pooling your resources across multiple projects or departments, you can take advantage of pricing breaks and reduce overhead costs.
- Example: AWS Organizations, Azure Management Groups, and Google Cloud’s Resource Hierarchy allow businesses to consolidate billing and manage costs at the organization level.
- Use Cost Allocation Tags and Resource Grouping
- What It Is: Tagging resources (e.g., instances, storage, databases) enables you to categorize and allocate costs more effectively. By tagging resources by project, department, or workload, you can gain clearer insights into which teams or projects are driving costs.
- How It Helps: These tags make it easier to identify areas of inefficiency and allocate resources more effectively. For example, you might discover that a particular project is consuming more cloud resources than expected, allowing you to investigate and optimize.
- Tools: AWS Cost Allocation Tags, Azure Tags, Google Cloud Labels.
- Rightsize and Optimize Data Storage
- What It Is: Cloud storage costs can add up quickly, especially if you’re storing large amounts of data that aren’t actively accessed.
- How It Helps: By choosing the right storage type (e.g., cold storage, archival storage) based on data access patterns, you can significantly reduce storage costs. You can also implement data lifecycle policies that automatically move data to lower-cost storage tiers over time.
- Example: AWS S3 offers different storage classes such as S3 Standard, S3 Infrequent Access, and S3 Glacier, each with varying costs depending on how often data is accessed.
Leveraging Cloud Cost Management Tools
There are a number of powerful tools and platforms available to help manage and optimize cloud costs:
- AWS Cost Explorer: Provides a detailed view of AWS spending, allowing you to analyze cost and usage patterns.
- Azure Cost Management and Billing: Helps track and manage Azure resources, with cost analysis and budgeting capabilities.
- Google Cloud Billing: Offers detailed billing reports and cost forecasting tools for GCP users.
For multi-cloud environments, platforms like CloudHealth by VMware and CloudCheckr can provide cross-cloud visibility and cost management.
Conclusion: Make Cloud Cost Optimization Part of Your Strategy
Cloud cost optimization is an ongoing process that requires careful monitoring, continual adjustment, and the adoption of the right tools. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your cloud spend is aligned with your needs — enabling you to scale, innovate, and grow while maintaining control over your budget. Start implementing these strategies today to unlock the true potential of your cloud investment, and watch your organization’s bottom line benefit from smarter cloud resource management.
Stay Updated
Subscribe to our newsletter for more insights into cloud strategies, trends, and cost-saving tips!
This blog post is a comprehensive overview of cloud cost optimization strategies, designed to be educational and actionable for businesses looking to make the most of their cloud environment. Feel free to adjust or add further examples to suit the tone and audience of your specific newsletter!