As businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, compliance with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS becomes a critical concern. Cloud providers play a pivotal role in helping organizations navigate these complex requirements, but achieving compliance in shared responsibility models presents unique challenges. Here’s a deep dive into how cloud providers address these regulatory challenges to ensure data security and legal compliance.
Understanding Compliance Requirements
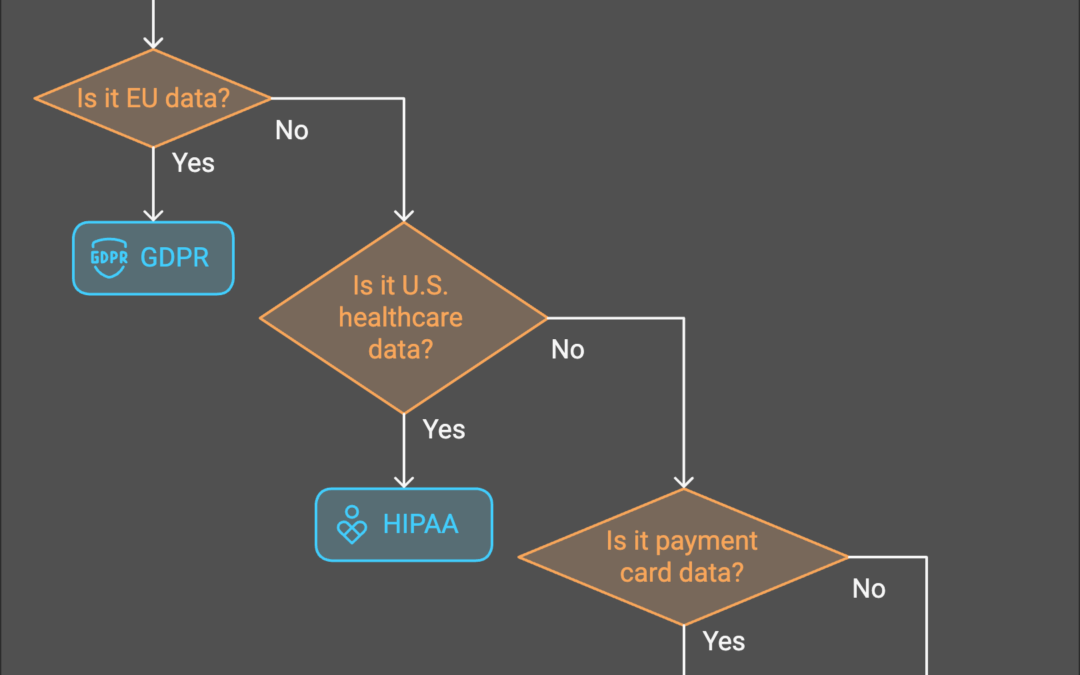
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Applicable to organizations handling data of EU (European Union) citizens, GDPR emphasizes data protection, transparency, and individual rights.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Designed for healthcare entities in the U.S., HIPAA mandates strict controls over Protected Health Information (PHI).
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Enforced for entities processing payment card data, this standard ensures secure handling of cardholder information.
Each of these frameworks requires robust mechanisms for data protection, access control, and incident response—areas where cloud providers must excel.
Challenges in Achieving Compliance
- Shared Responsibility Model: Cloud providers manage the infrastructure, but customers remain responsible for securing their applications and data.
- Data Residency and Sovereignty: Regulations like GDPR demand that data stay within specific regions, which can conflict with cloud providers’ global infrastructure.
- Auditing and Transparency: Businesses need detailed insights into how cloud providers handle compliance, creating pressure for better reporting and visibility.
- Evolving Standards: Regulatory frameworks are continuously updated, requiring cloud providers to stay agile in their compliance strategies.
How Cloud Providers Address These Challenges
1. Compliance-Centric Infrastructure
- Dedicated Data Centers: Cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have region-specific data centers to meet data residency requirements.
- Encryption at Rest and In Transit: Advanced encryption ensures data remains protected from unauthorized access, satisfying compliance needs.
2. Certifications and Audits
- Third-Party Certifications: Cloud providers undergo regular audits for certifications like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HITRUST, ensuring adherence to industry standards.
- Customer Trust Portals: Providers offer portals with audit reports and compliance documentation for customer reference.
3. Built-In Compliance Tools
- Preconfigured Templates: Cloud providers offer tools like AWS Config, Azure Policy, and Google’s Assured Workloads to automate compliance configurations.
- Monitoring and Alerts: Real-time monitoring solutions identify and report compliance risks.
4. Partnerships and Agreements
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): For HIPAA compliance, cloud providers enter BAAs with customers, delineating shared responsibilities.
- Data Processing Addendums (DPAs): Providers include DPAs to align with GDPR requirements, covering data handling and processing.
5. Incident Response Mechanisms
- Automated Backups and Recovery: Ensures data availability and integrity during breaches or outages.
- Security Operations Centers (SOCs): Cloud providers maintain 24/7 SOCs to monitor and mitigate threats in real time.
Real-World Examples
- GDPR Compliance: Google Cloud’s Assured Workloads allow customers to select specific data regions within the EU, ensuring GDPR adherence.
- HIPAA Compliance: AWS provides HIPAA-eligible services, like Amazon S3 and EC2, designed with enhanced access controls for PHI.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Microsoft Azure’s PCI DSS-compliant infrastructure enables secure payment processing and storage for e-commerce platforms.
Real-World Case Studies
- Dropbox and Security Breaches: Dropbox experienced multiple security breaches that exposed user data. This incident emphasized the need for robust security measures, including encryption and access control. Dropbox has since improved its security protocols and compliance practices, serving as a cautionary tale for other SMBs.
- Uber’s GDPR Fine: Uber faced a significant fine for failing to report a data breach to regulators as required under GDPR. This case illustrates the importance of understanding compliance obligations and maintaining clear communication channels regarding security incidents.
Best Practices for Organizations
- Understand Your Responsibilities: Use provider documentation to clarify what’s covered by the provider and what’s your responsibility.
- Leverage Compliance Tools: Automate configurations and continuously monitor for risks using provider-provided solutions.
- Collaborate Proactively: Engage with your provider to understand available resources and customize services for compliance needs.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Regularly assess your cloud environment against regulatory frameworks to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS is a collaborative effort between cloud providers and customers. By leveraging compliance-focused infrastructure, tools, and partnerships, cloud providers help organizations meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency. As compliance challenges evolve, proactive engagement with your cloud provider remains key to navigating this complex landscape successfully.